Nathan Yau from FlowingData has taken an in-depth look at the statistics behind How the Average Working Adult Spends Days in their lifetime.
There were some graphics going around that showed the total amount of time spent during an average person’s lifetime doing things. The numbers were pretty rough though.
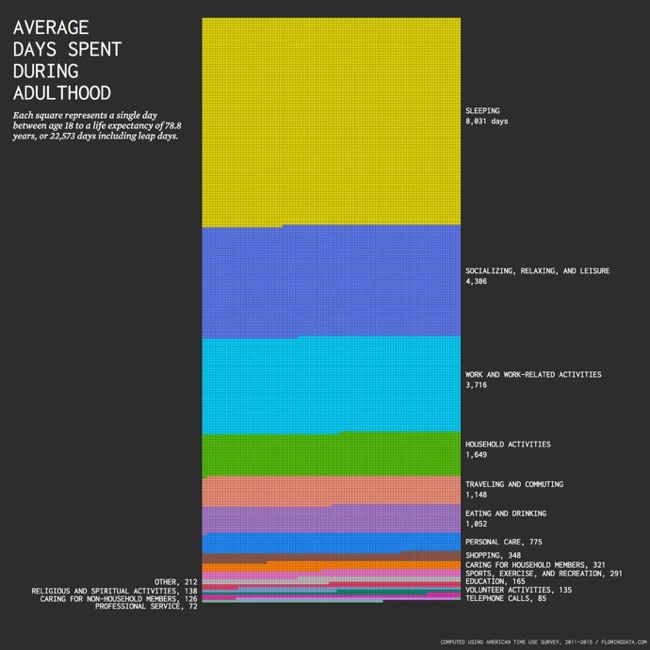
For example, to calculate the number of days spent sleeping during a lifetime, it was assumed that the average person sleeps eight hours per day, and then estimates just extrapolated for life expectancy. But sleep patterns change as you age. You start to sleep less as you get older.
So I tried taking this into account using data from the American Time Use Survey. I still used averages, but I calculated averages for each year of life and then aggregated. Here’s what I got for adulthood (18 and older) — the time you’re presumably making your own choices. Employment and retirement are assumed.
Again, these are still averages for an adult who works and then retires around 65 years, so the same caveats apply as usual. Everyone’s own totals will be a bit different, especially as you compare across groups. For example, the time distribution for parents looks different from the distribution for those who never have kids. Similarly, some never enter the labor force whereas others work full-time.
The data is from the American Time Use Survey, which is made more easily available from IPUMS. After downloading data for 2011 through 2015, I tabulated and charted in R. Also, maybe you noticed that the number of squares doesn’t quite add up to 22,573. This is due to rounding, which offset the total above by three days.
I prefer data visualizations like this that show the actual number of days as squares (or other shapes/icons) instead of summarizing them together into a stacked bar chart or a doughnut chart. Seeing the full number of days represented gives the readfers a better understanding of the true magnitude of the values being shown
Found on Big Think